Overclocking RAM can be a great way to improve the performance of your Ryzen system. It can reduce latency and improve bandwidth, leading to faster performance in games and other applications.
However, it’s important to note that overclocking RAM can also be risky. You can damage your RAM or entire system if you’re not careful. So, it’s important to do your research and proceed with caution.
If you’re a PC enthusiast or a gamer looking to squeeze every bit of performance out of your Ryzen-powered system, then overclocking your DDR4 RAM is a must-consider option.
Overclocking RAM can yield substantial performance gains and is relatively easy to do, especially with modern DDR4 memory and Ryzen processors. This guide will walk you through the steps to safely and effectively overclock your DDR4 RAM on a Ryzen system.
Here is a step-by-step guide on how to overclock DDR4 RAM on Ryzen:
Check your RAM’s specifications
Before you start overclocking, it’s important to check the specifications of your RAM. This will help you determine the maximum speed and timings that your RAM can.
You can usually find this information on the manufacturer’s website or your RAM’s packaging.
Update Your BIOS
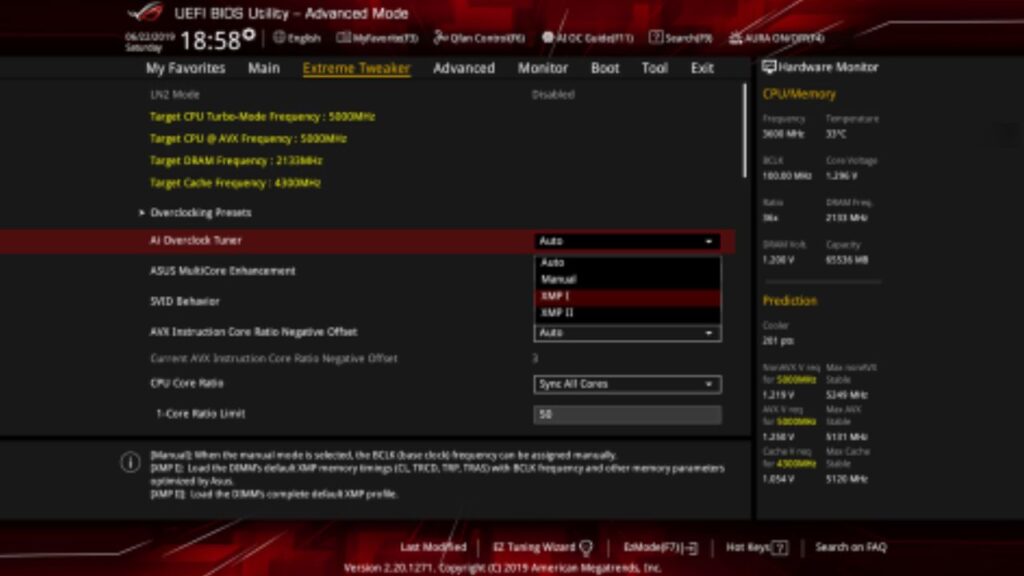
Once you know the specifications of your RAM, you need to enter your BIOS. This process varies depending on your motherboard manufacturer, so consult your motherboard manual for instructions.
If you’re looking for better performance in games, a BIOS update isn’t the way to go.
Find the memory settings
Once you’re in the BIOS, you must find the memory settings. These are usually located under a tab called “Memory” or “Overclocking.”
Set the memory frequency
The first thing you need to do is set the memory frequency. This is the speed at which your RAM will run.
Start by setting the frequency to the maximum speed that your RAM is rated for. For example, if your RAM is rated 3600MHz, set the frequency to 3600MHz.
Set the memory timings
The memory timings control the latency of your RAM. This is how long it takes for your RAM to access data.
Lower timings are better, but they can also be more difficult to achieve. Starting with the default timings is best if you’re new to overclocking.
Save your changes and exit the BIOS
Once you’re finished setting the memory frequency and timings, save your changes and exit the BIOS. Your computer will then restart.
Test your overclock
Once your computer has restarted, you must test your overclock to ensure it’s stable. You can use a program like MemTest86 to do this.
MemTest86 will test your RAM for errors. If you get errors, you must increase the memory timings or lower the frequency.
Continue tuning your overclock
You can tune it further once you’re confident your overclock is stable. This involves finding the highest possible memory frequency and timings at which your RAM is stable.
Check Your RAM Compatibility
Before you start overclocking your RAM, make sure your DDR4 modules are compatible with overclocking. Not all RAM sticks are created equal, and some may be unable to handle the increased frequencies and voltages required for overclocking.
Consult your RAM manufacturer’s website or documentation to verify if your RAM is overclockable.
Ensure Adequate Cooling
Overclocking generates more heat, and heat can damage your RAM modules over time. Ensure your system has adequate cooling solutions, including case fans and a good CPU cooler. If you plan to push your RAM to its limits, consider investing in RAM heatsinks or a RAM cooler.
Understand the Basics
Before diving into overclocking, it’s essential to understand a few key concepts:
a. Frequency (MHz): This is the speed at which your RAM operates. DDR4 RAM typically comes in 2133MHz, 2400MHz, 2666MHz, and higher frequencies. Overclocking will push this frequency higher.
b. Timings (CAS Latency, tRCD, tRP, tRAS): RAM timings refer to the delay between different operations within the RAM. Lower timings are better for performance but can become unstable when overclocked.
c. Voltage (V): Overclocking often requires increasing the voltage supplied to the RAM. Be cautious, as too much voltage can damage your RAM.
Start Slowly
Now that you’re prepared, it’s time to start overclocking:
a. Enter your motherboard’s BIOS/UEFI by pressing the designated key (usually Del or F2) during the boot process.
b. Locate the RAM settings in the BIOS. You may find options like “DRAM Frequency,” “Voltage,” and “Timings.”
c. Begin by increasing the RAM frequency incrementally. Start with a small increase, such as 100-200MHz.
d. Test your system’s stability after each increase. You can use benchmarking tools like MemTest86 or AIDA64 to check for stability. If your system crashes or experiences errors, reduce the frequency.
e. Once you’ve reached a stable frequency, you can fine-tune the timings for better performance. Be cautious here, as aggressive timings can lead to instability.
f. Gradually increase the RAM voltage if necessary to maintain stability, but never exceed the manufacturer’s recommended maximum voltage.
Monitor Temperatures and Stability
Throughout the overclocking process, monitor your system’s temperatures and stability. High temperatures can lead to instability, so ensure your cooling solution is adequate.
Additionally, monitor your system for crashes, errors, or unexpected behavior. If you encounter issues, revert to the previous settings.
Test Your System
After you’ve settled on an overclocked configuration that you’re satisfied with, it’s essential to thoroughly test your system for stability. Run stress tests and benchmarks to ensure your overclocked RAM can handle the workload.
It’s important to note that overclocking RAM is a trial-and-error process. There is no one-size-fits-all approach. You must experiment with different settings to find the best for your RAM.
Tips for Overclocking DDR4 RAM on Ryzen:
- Ryzen processors are very sensitive to the memory fabric clock. The memory fabric clock is the speed at which the CPU communicates with the RAM. Keeping the memory fabric clock and the memory frequency in sync is important.
- If you’re having trouble overclocking your RAM, try increasing the DRAM voltage. However, doing this is important, as too much voltage can damage your RAM.
- If you still have trouble overclocking your RAM, try using a tool like Ryzen DRAM Calculator. Ryzen DRAM Calculator can help you to calculate the optimal memory timings for your RAM.
Overclocking RAM can be a great way to improve the performance of your Ryzen system. However, it’s important to do your research and proceed with caution. You can damage your RAM or entire system if you’re not careful.
Conclusion:
Overclocking your DDR4 RAM on a Ryzen system can yield significant performance gains, but it’s not without risks. It’s essential to approach the process cautiously, follow the manufacturer’s recommendations, and monitor your system’s stability and temperatures.
With the right knowledge and care, you can unlock the full potential of your RAM and enjoy a more powerful computing experience. Happy overclocking!