In the intricate world of computer hardware, the choice of Random Access Memory (RAM) modules goes beyond just capacity.
Among the decisions to make is whether to opt for Single-Sided (SS) or Double-Sided (DS) RAM modules.
In this article, we’ll unravel the mysteries behind these configurations, exploring the differences, advantages, and considerations that can impact your computing experience.
Understanding the Basics:
RAM, the essential memory component that keeps your system running smoothly, comes in various forms. DS vs SS RAM Ryzen refers to the physical layout of the memory chips on the RAM module.
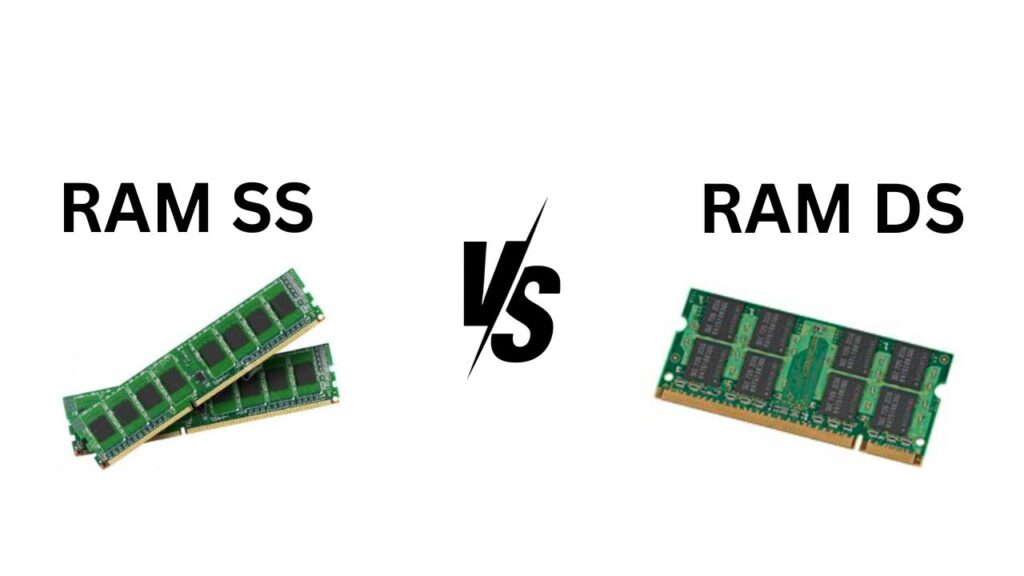
Single-Sided (SS):
In Single-Sided configurations, memory chips are located on only one side of the RAM module. This setup is often visually apparent, as the back of the module remains devoid of components.
Advantages of Single-Sided:
- Lower Power Consumption: Single-Sided modules generally consume less power since there’s only one side of memory chips to power.
- Compatibility: They are more compatible with certain systems that have limited space or restrictions on the number of chips per side.
Double-Sided (DS):
Double-Sided RAM modules, as the name suggests, have memory chips on both sides of the module. This configuration is common in higher-capacity modules.
Advantages of Double-Sided:
- Higher Capacities: Double-Sided modules can accommodate more memory chips, allowing for higher capacity options.
- Balanced Heat Distribution: With chips on both sides, heat dissipation may be more evenly distributed, potentially contributing to better temperature management.
Performance and Considerations:
When it comes to raw performance, the distinction between RAM SS vs DS Ryzen modules might be less noticeable in everyday computing tasks.
However, there are factors to consider depending on your specific use case:
1. Memory Capacity Needs: Single-Sided modules are often sufficient for moderate computing needs, but if you require higher capacities for demanding applications or multitasking, Double-Sided configurations may be more suitable.
2. Thermal Considerations: Single-Sided modules may have an advantage in terms of lower power consumption and potentially lower temperatures. If heat management is a concern, this could be a relevant factor.
3. Motherboard Compatibility: Some motherboards may have restrictions on the number of Double-Sided modules they can support or may require specific configurations for optimal performance.
Conclusion:
In the SS vs DS RAM module debate, the decision hinges on your specific requirements and preferences.
For everyday computing tasks, Single-Sided configurations may offer a balanced solution. Still, if you’re delving into resource-intensive applications or seeking higher capacities, Double-Sided RAM might be the way to go.
Ultimately, understanding your system’s needs, considering compatibility, and weighing the advantages of each configuration will guide you in making an informed decision.
The journey into the world of RAM modules is a fascinating one, where the right choice can enhance your computing experience. Comment here.