Both microprocessors and microcontrollers are types of electronic devices that come in the form of integrated circuits (ICs) and are used in different modern electronic equipment such as laptops, computers, air conditioners, washing machines, and many other automated electronic gadgets.
The primary function of both microprocessors and microcontrollers is to automate the processes.
Please read this article to find out more about microprocessors and microcontrollers and how they are different from each other.
What is a Microprocessor?
As its name implies, it is a processing device that converts data into information based on some sets of instructions.
It is a very compact electronic chip, due to which it is referred to as the microprocessor. In other words, a processing device implemented on a single chip is called a microprocessor.
A microprocessor is the most crucial component of a computer or any other computing device because it is entirely responsible for processing data based on instructions to produce information.
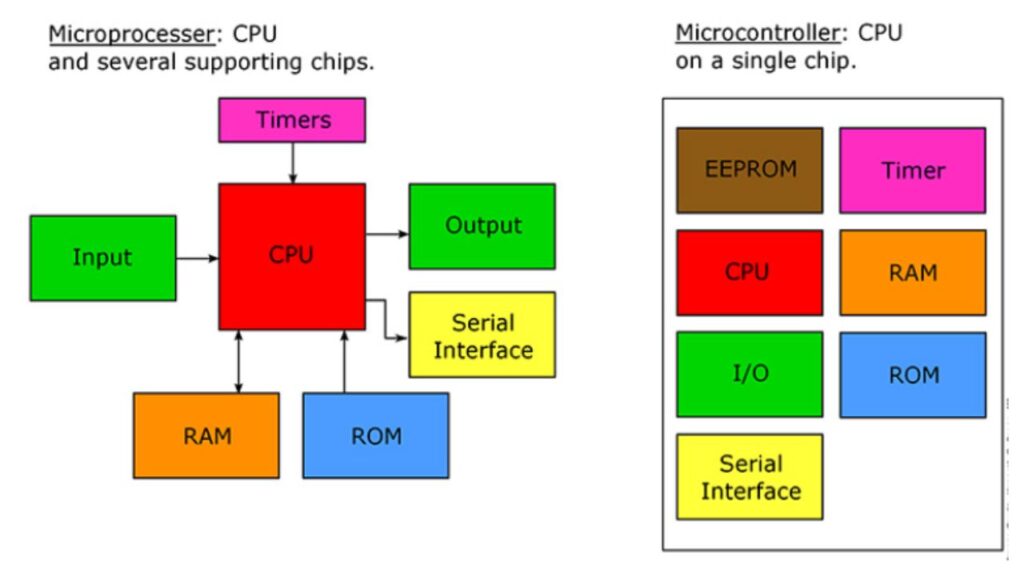
In microcomputers, the microprocessor is used as the CPU (Central Processing Unit). A typical microprocessor consists of two major parts, namely ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit) and CU (Control Unit).
Intel 8085 or 8086 processing chips are examples of microprocessors. Modern microprocessors consist of a small memory unit (cache memory) in addition to the ALU and CU.
Nowadays, microprocessors are being widely used in several applications such as desktop publishing, power plant control, multimeters, medical instruments, etc.
What is a Microcontroller?
A microcontroller is an electronic system that consists of a processing element, a small memory (RAM, ROM, EPROM), I/O ports, etc., on a single chip. Therefore, a microcontroller is a tiny resemblance to a microcomputer.
It is a quite small and low−cost electronic device that is used in several electronic appliances as the main functioning device.
In electronic systems such as washing machines, air conditioners, refrigerators, etc., microcontrollers are used to automate the operation of the device based on the user’s instructions.
Hence, a microcontroller is the backbone of all embedded systems like microwave ovens, washing machines, smart refrigerators, etc.
Microprocessors find their application in light sensing and controlling devices, temperature sensing and controlling devices, fire detection and other safety devices, smart measuring instruments, etc.
Microprocessors: The Brains of the Computer
Firstly, microprocessors are the heart of modern computers and many high-performance electronic devices.
They are essentially the central processing unit (CPU) and handle the execution of instructions and calculations required for running software and applications.
Here are some of the primary characteristics of microprocessors:
- General-Purpose: Microprocessors are designed to handle a wide range of tasks and are capable of executing complex instructions. They are found in desktop computers, laptops, servers, and other computing devices.
- External Components: Microprocessors typically require external components such as memory (RAM and ROM), input/output (I/O) interfaces, and peripherals to function effectively. These components are connected externally to the microprocessor.
- Operating Systems: Microprocessors often run full-fledged operating systems like Windows, Linux, or macOS, which provide a platform for running various software applications.
- Processing Power: Microprocessors are optimized for high processing power and are designed to execute instructions at a rapid pace. This makes them suitable for tasks like multitasking, gaming, and complex computations.
Microcontrollers: Embedded Brains for Specific Tasks
Microcontrollers, on the other hand, are compact computing devices tailored for specific applications.
They combine a processor core with memory, input/output peripherals, and often, real-time control capabilities.
Let’s take a closer look at the characteristics of microcontrollers:
- Specialized Purpose: Microcontrollers are designed for specific tasks or applications, such as controlling appliances, automotive systems, medical devices, or industrial machinery.
- Integrated Components: Unlike microprocessors, microcontrollers have all necessary components, including CPU, RAM, ROM, timers, counters, and I/O ports, integrated into a single chip. This integration reduces the need for external components.
- Real-Time Processing: Many microcontrollers are capable of real-time processing, which means they can respond to inputs and perform actions with minimal delay. This feature is crucial for applications where timing is critical.
- Low Power Consumption: Microcontrollers are often optimized for power efficiency, making them suitable for battery-powered or energy-efficient devices.
- No Operating System: Unlike microprocessors, microcontrollers usually do not run full-fledged operating systems. Instead, they typically run a program or firmware designed explicitly for the application they serve.
Difference between Microprocessor and Microcontroller
The important differences between microprocessor and microcontroller −
| Microprocessor | Microcontroller |
| Microprocessors can be understood as the heart of a computer system. | Microcontrollers can be understood as the heart of an embedded system. |
| A microprocessor is a processor where the memory and I/O component are connected externally. | A microcontroller is a controlling device wherein the memory and I/O output component are present internally. |
| Microprocessors are not efficient. | Microcontrollers are efficient. |
| Microprocessors have a zero status flag. | Microcontroller doesn’t have a zero status flag. |
| It is mainly used in personal computers. | It is used mainly in washing machines, MP3 players, and embedded systems. |
| Microprocessors can’t be used in compact system. | Microcontrollers can be used with a compact system. |
| The memory and I/O components are to be connected externally. | The memory and I/O components are available. |
| Microprocessors are generally used in personal computers. | Microcontrollers are generally used in washing machines, and air conditioners. |
| The circuit is complex due to external connection. | Microcontrollers are present on chip memory. The circuit is less complex. |
| It has no ROM, RAM, Input-Output units, timers, and other peripherals on the chip. | It has a CPU along with ROM, RAM, and other peripherals embedded on a single chip. |
| Microprocessors have less number of registers. Not cost-effective | Microcontrollers have more number of registers. Cost-effective |
Types of Microprocessor
Here are Important types of Microprocessors:
- Complex Instruction Set Microprocessors
- Application-Specific Integrated Circuit
- Reduced Instruction Set Microprocessors
- Digital Signal Multiprocessors (DSPs)
Types of Microcontroller
Important types of Microcontroller are:
- 8-bit Microcontroller
- 16-bit Microcontroller
- 32-bit Microcontroller
- External memory Microcontroller
- Embedded Microcontroller
Conclusion:
From the above discussion, it is clear that a microprocessor is an electronic component that acts as a processing device in various computing systems such as computers, laptops, smartphones, etc.
Microprocessors drive the power and versatility of our computers, while microcontrollers enable the intelligence behind everyday devices and systems.
On the other hand, a microcontroller is a small microcomputer that acts as a controlling device in different embedded systems such as washing machines, microwave ovens, etc. Comment here.
For more article visit – >>> Supercomputer and Quantum Computer