In the world of computing, the number of CPU cores and threads your system possesses can significantly impact its performance.
Whether you’re a gamer, a content creator, or just a regular computer user, knowing how many CPU threads you have is valuable information.
In this article, we’ll explore various methods to check how many CPU cores and threads your system has on a Windows PC.
How Do I Check My CPU and Cores on Windows?
Checking the number of CPU cores and threads on your Windows PC can be done through several methods.
Let’s delve into each of them.
Searching the manufacturer’s information
- Check Your System Documentation: The easiest way to determine your CPU’s specifications, including the number of cores and threads, is to refer to your computer’s documentation. If you have a pre-built computer, the manufacturer’s website may also provide detailed information about your system’s hardware.
- Look on the CPU: If you’re using a custom-built PC, you can open your computer case and visually inspect the CPU. Most modern CPUs have the core and thread information printed directly on the CPU’s integrated heat spreader (IHS).
Find Out How Many Cores Your Processor has(Windows 10)
Use of Task Manager
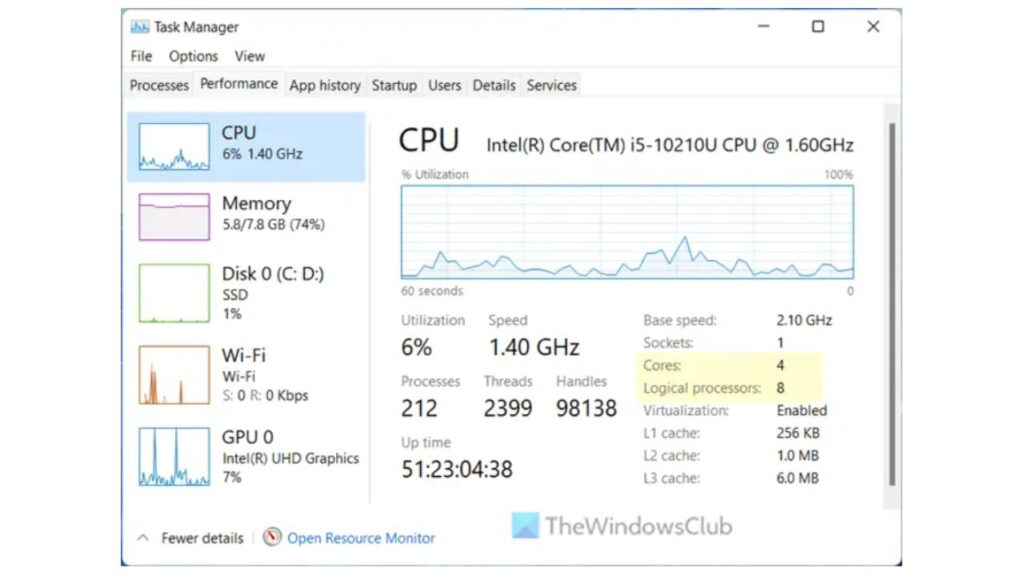
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc: This key combination opens the Task Manager.
- Navigate to the Performance tab: Click on the “Performance” tab in Task Manager.
- Check CPU Information: Under the “CPU” section, you’ll find information about the number of sockets, cores, and logical processors (threads).
Using Device Manager
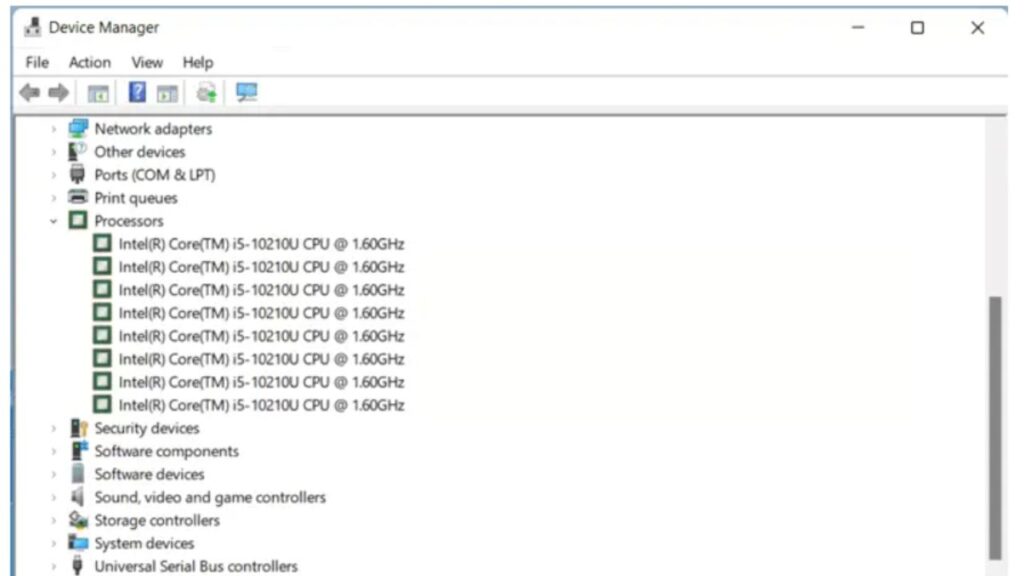
The device manager also maintains track of your CPU’s specifications, and you can check the thread count of your particular processor in real-time.
1. Press Windows Key + X and click on Device Manager.
2. Expand the Processors section; the number of processors you see is the total count of threads.
Use of Run Command

- Press Win + R: This opens the Run dialog box.
- Type “DXdiag” and press Enter: It opens the DirectX Diagnostic Tool, which provides detailed information about your CPU under the “Processor” tab.
Use of Command Prompt
- Press Win + X: This opens the Power User menu.
- Select Command Prompt (Admin) or Windows Terminal (Admin): Choose either of these options to open a command prompt with administrative privileges.
- Type “wmic cpu get caption, device id, number of cores, number of logical processors” and press Enter: This command will display detailed CPU information, including the number of cores and logical processors.
What Is Multi-Threading?
Before we move on to more methods of checking CPU threads, let’s briefly explain multi-threading. Multi-threading is a technology that allows a CPU to execute multiple threads (or tasks) simultaneously.
Each thread represents an independent unit of work, and modern CPUs can have multiple threads per core. This technology significantly improves multitasking and overall system performance.
Using Third Party Software
While the methods mentioned above provide native ways to check your CPU’s core and thread count, you can also use third-party software for more detailed information and monitoring.
Task Manager in Windows OS
- Right-click on the taskbar: This opens a context menu.
- Select Task Manager: Task Manager will open.
- Navigate to the Performance tab: Similar to the native Task Manager, you can find CPU information, including the number of logical processors (threads) here.
Check the number of Logical Processors
- Press Win + Pause/Break: This opens the System window.
- Look under “System” information: You’ll find details about the number of logical processors (threads) here.
Specifications for CPUs
- Download CPU-Z: CPU-Z is a popular third-party tool that provides in-depth information about your CPU, including the number of cores and threads.
- Install and run CPU-Z: After installation, run the software, and you’ll find comprehensive details about your CPU under the “CPU” tab.
How Many Cores and Threads Does My CPU Have?
It’s important to note that the number of cores and threads can vary widely depending on your CPU model.
Some CPUs have as few as two cores and four threads, while high-end CPUs can have up to 64 cores and 128 threads.
Checking your CPU model and referring to the manufacturer’s website or documentation is the most accurate way to determine your CPU’s core and thread count.
System information in Windows OS
- Press Win + R: This opens the Run dialog box.
- Type “msinfo32” and press Enter: The System Information utility will open.
- Expand “Components” and click on “Processor.”: Here, you’ll find detailed information about your CPU, including the number of cores and threads.
FAQs
Which CPU model has the most threads?
As of my last knowledge update in September 2023, some of the high-end CPUs with the most threads include the AMD Ryzen Threadripper series and the Intel Xeon Platinum series.
However, CPU models are continually evolving, so it’s essential to check the latest releases for the most up-to-date information.
How many threads do 4 cores have?
The number of threads in a CPU with 4 cores can vary depending on whether the CPU supports hyper-threading or simultaneous multi-threading (SMT).
If it does, a 4-core CPU can have 8 threads, as each core can handle two threads simultaneously. If the CPU doesn’t support hyper-threading, it will have 4 threads.
Is there a CPU with 128 cores?
Yes, as of my last knowledge update, there are CPUs with 128 cores available in the market, such as some models in the AMD EPYC server processor series. These high-core-count CPUs are primarily designed for data centers and enterprise-level computing.
How can I monitor CPU usage and thread count on my computer?
To monitor CPU usage and thread count on your computer, you can use built-in tools like Task Manager or third-party monitoring software.
Task Manager provides real-time information about CPU usage and the number of logical processors (threads).
Additionally, third-party software like HWMonitor, CPU-Z, or Core Temp offers more detailed monitoring options and historical data.
Conclusion:
Knowing how many CPU cores and threads your computer has is crucial for understanding its capabilities and optimizing its performance.
You can check this information through various methods on a Windows PC, including built-in tools like Task Manager, the Run command, and the Command Prompt. Additionally, third-party software can provide more detailed insights into your CPU’s specifications.
Keep in mind that CPU technology continues to advance, so it’s a good idea to check for the latest CPU models and their capabilities if you’re planning to upgrade your system for specific tasks or applications. Comment here.

