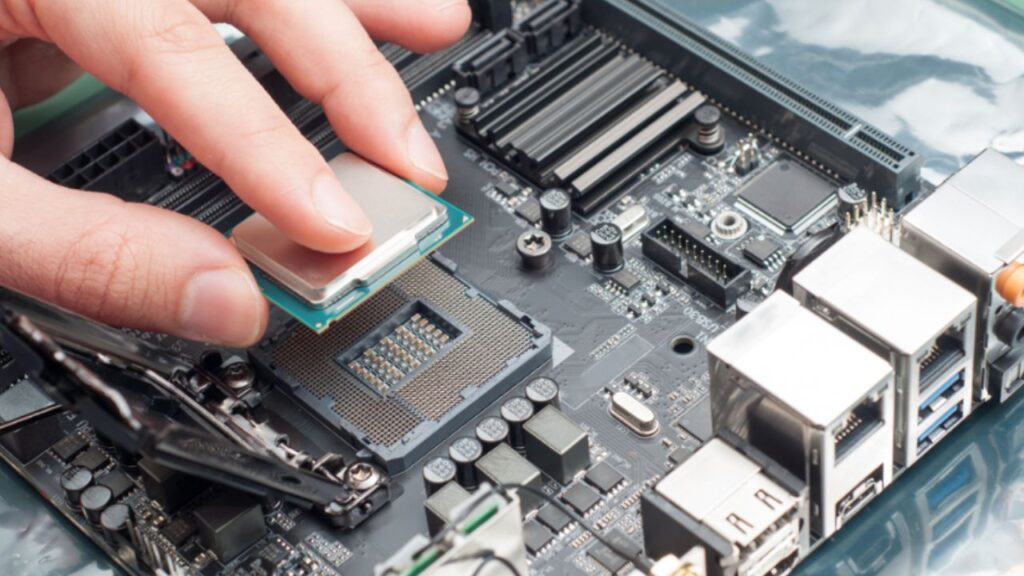
The computer’s brain, the CPU, needs a stable and secure home. Enter the CPU socket: the unsung hero of every desktop PC, silently holding the processor in place and facilitating its communication with the rest of the hardware.
However, if you are new to building or upgrading your computer, the world of sockets can seem daunting.
Fear not! This article will demystify what a intel CPU socket types list is, why it matters, and how to navigate the different types.
What is a Socket in CPU?
A CPU socket, also known as a processor socket, is a specific mechanical component on a motherboard designed to house and connect the CPU.
Think of it as the interface that allows the CPU to communicate with the other components on the motherboard, such as the memory, graphics card, and storage devices.
The socket is essentially a receptacle that holds the CPU in place and facilitates the transfer of data and power between the CPU and the rest of the system.
Importance of CPU Sockets
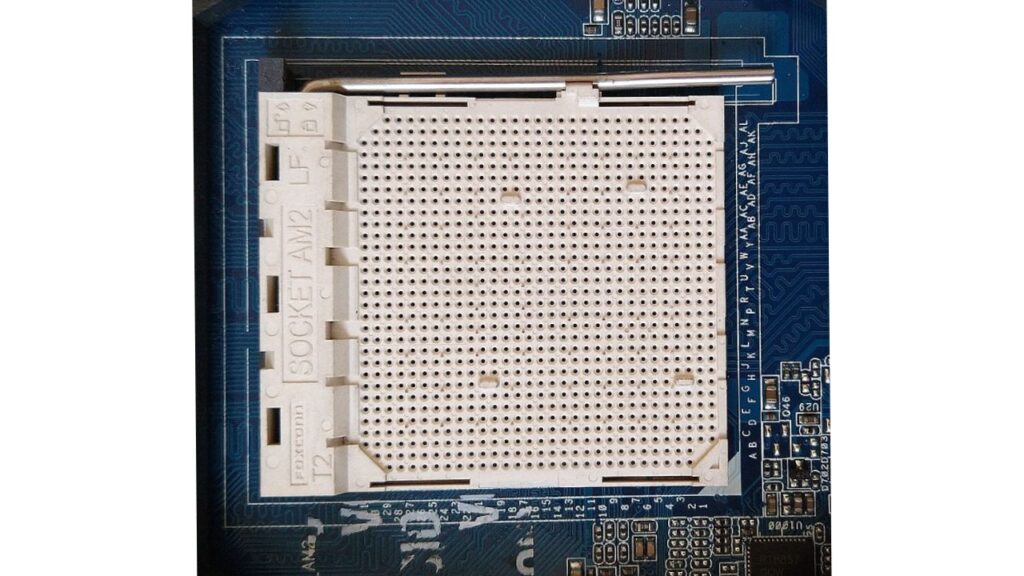

The significance of CPU sockets is paramount in shaping the functionality and upgradability of a computer system. These sockets establish a standardized method for connecting CPUs to motherboards, guaranteeing compatibility across various CPU and motherboard models.
This compatibility feature enables users to seamlessly upgrade or replace their CPUs without the necessity of changing the entire motherboard.
This approach proves to be both cost-effective and convenient, offering an efficient means to enhance overall system performance.
Beyond facilitating compatibility, CPU sockets exert influence over crucial aspects like heat dissipation, power delivery, and data transfer rates.
Their role extends beyond mere connectivity, impacting the overall performance and efficiency of a computer system.
In essence, CPU sockets serve as a linchpin in the intricate web of components that contribute to the seamless operation of modern computing devices.
History of CPU Sockets
The history of CPU sockets is a compelling narrative that chronicles the transformative journey of computer hardware.
As the central processing units (CPUs) evolved in terms of performance and architecture, so did the interfaces connecting them to motherboards.
This historical overview delves into the key milestones that have shaped the evolution of CPU sockets.
Early Era (1970s-1980s):
The nascent days of computing witnessed CPUs directly soldered onto motherboards, limiting flexibility and upgrade options. This era laid the groundwork for the exploration of socketed designs to facilitate easier upgrades.
Socket 1 and Socket 2 (Intel, 1989):
Intel’s introduction of Socket 1 marked a departure from soldered CPUs, providing a standardized interface for 486 processors. Socket 2 followed with incremental improvements, offering users a more adaptable platform for CPU upgrades.
Socket 7 (Intel, 1994):
The Socket 7 era emerged as a pivotal phase, supporting Intel’s Pentium and Pentium MMX CPUs. Its compatibility with processors from various manufacturers, including AMD and Cyrix, made it a popular choice for users seeking enhanced performance.
Slot 1 and Slot A (Intel & AMD, 1997):
A brief divergence from traditional sockets occurred with the introduction of Slot 1 for Intel’s Pentium II and Slot A for AMD’s Athlon CPUs. This cartridge-style design was short-lived, as industry trends favored a return to traditional socket configurations.
PGA vs. LGA (2000s-2010s):
The battle between Pin Grid Array (PGA) and Land Grid Array (LGA) designs gained prominence. Intel championed LGA sockets, offering simplified CPU installation and improved electrical contact reliability. AMD, in contrast, continued to utilize PGA sockets.
Modern Sockets (2010s-2020s):
The contemporary landscape features ongoing evolution in CPU sockets. Notable examples include:
- Intel’s LGA 1151 and AMD’s AM4 sockets which accommodate.
- Accommodating advancements in power delivery.
- Data transfer rates.
- Integrated graphics capabilities.
Socket Compatibility and Future Prospects:
In the present era, backward compatibility remains a key focus for motherboard manufacturers. Users can upgrade CPUs without replacing their entire systems, underscoring the commitment to user-friendly and customizable computing experiences.
Looking forward, future CPU sockets are expected to incorporate innovations in power efficiency, data transfer technologies, and compatibility with emerging hardware standards.
Key Components of a IGA CPU Socket
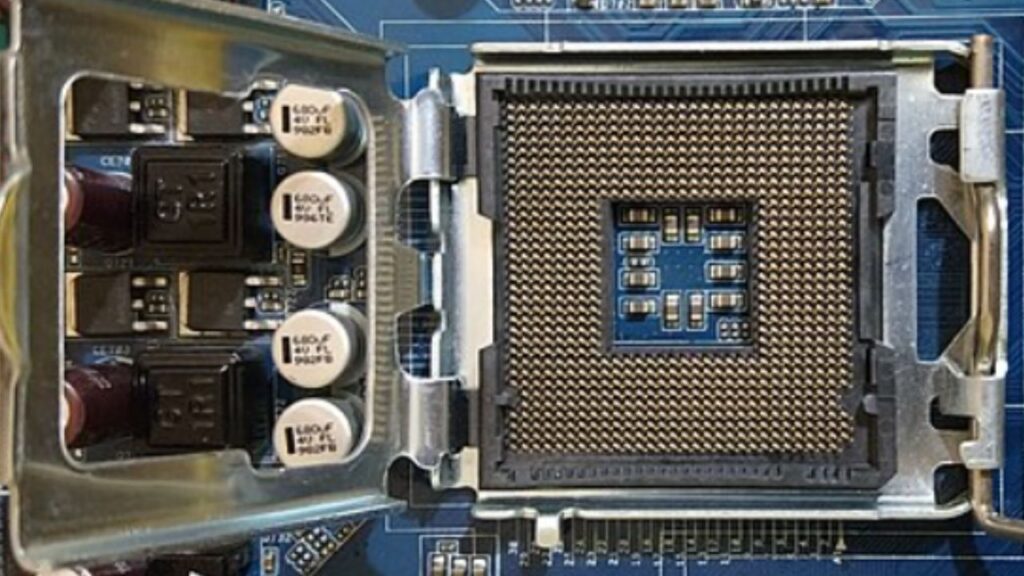

- Pin Grid Array (PGA) or Land Grid Array (LGA): CPU sockets come in two main designs – PGA and LGA. PGA sockets have an array of pins on the motherboard that directly connect with the corresponding holes on the underside of the CPU. On the other hand, LGA sockets have flat pads on the CPU, and the motherboard contains pins that make contact with these pads. Intel predominantly uses LGA sockets, while AMD typically employs PGA sockets.
- Mounting Mechanism: The socket features a securing mechanism, often in the form of a lever, that holds the CPU firmly in place. This ensures proper alignment and contact between the CPU and the socket.
- Power Delivery and Data Transfer: The CPU socket is responsible for supplying power to the CPU and facilitating data transfer between the CPU and other components. This includes communication with the memory, graphics card, and other peripherals.
Significance of CPU Sockets
- Compatibility: CPU sockets play a crucial role in determining which CPUs are compatible with a particular motherboard. Different CPU models require specific AMD socket types, and using an incompatible CPU can result in system failure.
- Upgradability: As technology advances, new CPU models with improved performance and capabilities are released. A standardized socket allows users to upgrade their CPU without replacing the entire motherboard, offering a cost-effective way to enhance system performance.
- Cooling Solutions: The design of the CPU socket influences the compatibility of cooling solutions. Heat sinks and fans, crucial for maintaining optimal CPU temperatures, must align with the socket’s layout.
CPU Socket Compatibility:
Not all sockets are created equal. Each type is designed for specific CPU families (e.g., Intel’s LGA 1700 for 12th Gen Core CPUs). Matching the socket and CPU is crucial for a functional computer. So, when choosing a motherboard and CPU, always ensure compatibility!
Popular CPU Socket Types:
In today’s landscape, some familiar faces dominate the socket scene:
- Intel: LGA 1700 is for current mainstream CPUs, and LGA 1200 is for the previous generation.
- AMD: AM4 for Ryzen processors, with the upcoming AM5 socket on the horizon.
Choosing the Right CPU Socket:
Remember, the socket choice hinges on your CPU preference and future upgrade plans. Do some research before buying, and consult online compatibility tools for peace of mind.
So, the next time you hear “CPU socket,” picture it as a friendly handshake between your processor and the motherboard. It is the foundation for a thriving computer, allowing you to tinker, upgrade, and keep your tech adventures going!
This blog article is just a starting point. Feel free to explore further to learn about specific socket types, compatibility checkers, and exciting upgrade possibilities. Happy building!
The Importance of a Socket:
Imagine soldering your CPU directly to the motherboard – a permanent marriage for better or worse. That is exactly what laptops do, sacrificing upgradeability for compactness.
Thankfully, desktops embrace the freedom of the socket: a physical connector on the motherboard designed to house the CPU.
- Easy Upgrades: When your tech cravings demand a faster processor, swap out the CPU – no need to replace the entire motherboard.
- Variety of Choices: Sockets cater to a range of CPU types, giving you flexibility when building your dream rig.
- Repair Potential: A faulty CPU can be replaced instead of scrapping the whole motherboard.
Conclusion:
In summary, the CPU socket is a fundamental component that establishes the vital connection between the CPU and the motherboard.
Its design, whether PGA or LGA, determines compatibility, upgradability, and the effectiveness of cooling solutions.
As technology continues to evolve, CPU sockets will play a pivotal role in shaping the landscape of computer hardware, ensuring that users can harness the power of the latest and greatest CPUs in their systems.
Whether you are a seasoned enthusiast or a casual user, understanding the significance of CPU sockets is essential for building and maintaining a high-performance computer. Comment here.